holy rummy Have you ever found yourself giving into a spontaneous desire to make a purchase because an advertisement impressed you, the packaging appealed to you, or something just nudged you? Most likely, yes. Harvard studies suggest that 95% of purchasing decisions are made subconsciously, emotionally. And companies have learned to work with this, utilizing neuromarketing. holy rummy
1. Why Neuromarketing is Needed holy rummy
The precursor to neuromarketing was the research conducted in the late 1970s by American psychologists Daniel Kahneman and Amos Tversky, who were the first to study how people use heuristics — processes that facilitate the discovery of new insights — in decision-making and the cognitive biases — errors in thinking that arise because the brain simplifies information. holy rummy
The research by Daniel Kahneman and Amos Tversky drew attention from practitioners and theorists to the psychological aspects of decision-making. Previously, it was assumed that consumer behavior could be controlled by a simple mathematical function, and their experiments, especially the prospect theory, although not directly related to the situation of consumer choice, fundamentally changed the angle from which economists view humans. Their research was further deepened by other scientists. holy rummy
Eventually, scientific theories interested marketers who assume that it is possible to study consumer brain reactions and apply them in marketing to achieve a more predictable result of irrational choice.
The term “neuromarketing” first appeared in 2002 — introduced by Professor Ale Smidts of Erasmus University Rotterdam.

Neuromarketing is the study of unconscious factors that influence the purchasing decision — smells, colors, sounds, tastes, touch. . This field combines knowledge from cognitive psychology, neurophysiology, and marketing.
2. How Neuromarketing Works holy rummy
Research into the human neural system comes into play.

2.3 Smell: the scent in the store.
Scents are effective because information about them reaches the brain faster than signals from eyes and ears.
2.4 Taste of the Product and Tactile Perception
These also matter.
It’s important to consider a number of parameters. For example, the correlation between a consumer’s reaction and their judgments when they do not align. Or the change in brain activity during the selection process from several offered options. . Memory is also one of the key research factors—what the consumer remembers after contact with the brand. All this helps make the product or service as attractive as possible.
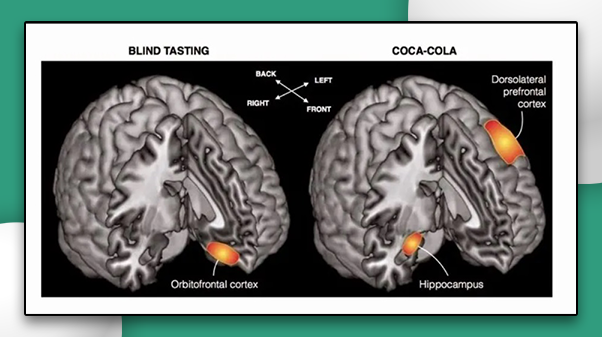
One of the most powerful cognitive biases marketers use is anchoring. It represents a form of cognitive bias that, when making decisions, makes people focus on the initial information available. It works particularly well with pricing when the seller sets one price serving as an anchor, then announces a lower price.
After that, he announced that the actual price of the new product would start at $499. The figure on the screen changed, and the price seemed to magically drop by half. Another marketing trick is the dopamine loop. It arises in anticipation of something interesting, desirable, especially actively in response to an unexpected reward.
3. How Neuromarketing is Used in Advertising
Emotional Engagement through Visual Stimuli: Leveraging neuromarketing insights, companies can craft advertising campaigns that effectively evoke strong emotional responses from their target audience. For instance, advertisements for children’s products often utilize images of happy children and parents to provoke feelings of warmth and care, increasing the likelihood of a purchase.
CTA Optimization Using Color Psychology: Neuromarketing can help determine which colors are most effective in drawing attention to call-to-action (CTA) buttons in ads and on websites. For example, employing a red color for a “Buy Now” button can heighten a sense of urgency and stimulate immediate purchases due to its ability to elevate alertness and arousal.
Content Personalization Based on Cognitive Preferences: By analyzing how different types of content impact brain activity, companies can create more personalized advertisements that speak directly to the interests and preferences of their target audience. For example, if research shows that a specific audience responds better to overcoming challenges, advertising campaigns can include narratives about how products helped people overcome obstacles.
4. How Neuromarketing Research is Conducted and With What Devices
Neuromarketing utilizes several types of biometrics to track consumer reactions. These include respiratory rate, even minor sweating, changes in pulse, direction of gaze, facial expressions, and brain electrical activity. Studies combine, examining various parameters, but not necessarily all, to obtain a more complete picture. Technologies that help visualize physiological reactions are used for this purpose.
4.1 Eye Tracking
A special camera records eye movement, gaze direction, and pupil dilation. These indicators can evaluate, for example, which part of the screen viewers’ gaze lingers on during an advertisement, allowing the most important information to be placed accordingly. Or it can optimize brand colors, packaging design, or shelf layout.

Types of eye-tracking equipment:
a) glasses for visual monitoring;
b) headband device;
c) helmet device;
d) remote control and management devices.
4.2 Galvanometer
Measures skin electrical activity, or skin galvanic response. The device is placed on the hand or finger and assesses the level of arousal and cognitive load — memory engagement when interacting with the brand. This helps optimize the advertising campaign based on what causes the audience the most arousal.
A polygraph can also capture emotional reaction, heart rate, breathing rate, and skin electrical activity.
4.3 Skin galvanic response sensor. High-resolution Photo and Video Cameras
In combination with software applications based on the Facial Action Coding System (FACS). Such cameras capture, and machine algorithms recognize the subject’s facial expressions and correlate them with a specific emotion triggered by the reaction to what is seen.
Example of a mobile laboratory Face reading work — an emotion assessment system using automatic recognition of human facial micro-expressions — to determine advertising effectiveness.
Leave a request for a free consultation with our marketing agency WGG, and we will develop an individual plan for your business promotion for you!


